- Hygetropin 200iu
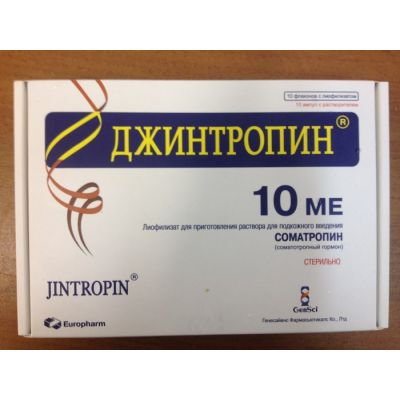
- Jintropin
- Igtropin
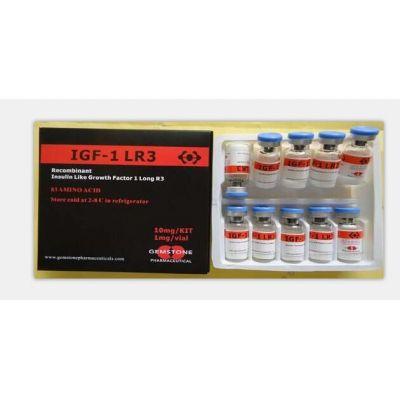
- IGF
- HCG
- Taitropin
- Riptropin
- Kigtropin
- Peptides
- Ansomone
- Angtropin
- Steroid
- HMG Memotropins For Injection
- Methenolone Enanthate Drostanolone Enanthate
- Testosterone Enanthate
- Testosterone Cypionate
- Trenbolone Acetate
- Dianabol
- Oxandrolone
- Haratropin
- Stanozolol
- RAW POWDER
- Trenbolone Acetate Trenbolone Enanthate
- Methandienone(Methandrostenolone)
- Testosterone Decanoate
- Boldenone Undecylenate
- Angtropin 200iu
- Anadrol-Oxymetholone raw powder
- Blue top
- Nuptropin
- Bestropin
- Brown top hygetropin 100iu
- SARMS products
- IGF
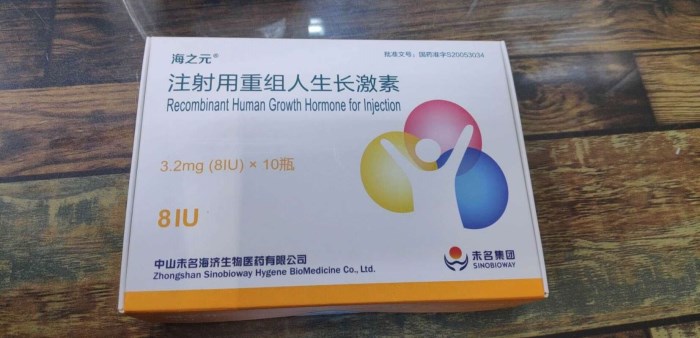
- Sinotropin haizhiyuan
Product name : Sinotropin haizhiyuan 海之元
| Details : | |
Recombinant Human Growth Hormone for Injection (rhGH) Please read the package insert carefully and follow the guidance of the physician
【DRUG NAME】 Generic name: Recombinant Human Growth Hormone for Injection Brand name: Sinotropin 【COMPOSITION】 The active ingredient is the recombinant human growth hormone, which is composed of 191 amino acids with a molecular weight of 22,125 Da. The excipients consist of glycine 0.68 mg, mannitol 18 mg, and a moderate amount of sodium dihydrogen phosphate and sodium hydrogen phosphate. 【CHARACTER】 The drug is white lyophilized powder. 【INDICATION】 The drug is indicated for children with growth failure due to the endogenous growth hormone deficiency (GHD). 【SPECIFICATION】 1.0mg(2.5IU) /vial, 1.6mg(4IU) /vial, 3.2mg(8IU) /vial 【DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION】 The lyophilized rhGH is dissolved in the attached 1 ml sterilizing water for injection. Shake slightly to dissolve the powder. The solution should be clear liquid. Do not use the product if the solution is muddy or has particles. Avoid violent oscillation. The dose is different from person to person. The recommended dose for subcutaneous injections is 0.1IU/kg/d. The subcutaneous injection should be administered at bedtime daily, or as directed by the doctor's advice. The injection site should be changed frequently to avoid injection site fat atrophy. 【ADVERSE REACTIONS】 Growth hormone can cause the transient hyperglycemia, which usually returns normal after the extended treatment or treatment termination. Clinical trials showed side effects in 1% of children with short stature. The most common adverse reactions are injection site reactions (e.g. pain, numbness, redness, and swelling) and fluid retention (e.g. peripheral edema, arthralgia, or myalgia). These side effects occur in the earlier stage of the treatment and rarely influence the daily activities. The frequency of side effects reduces over time. Injecting the recombinant human growth hormone for a long time will form antibodies in a minority of patients but the antibody binding force is low, indicating no exact clinical significance. Antibodies may be produced if the expected growth effect is not achieved. If the antibody binding force is more than 2 mg/L, it may affect the efficacy of the treatment. 【CONTRAINDICATION】 1. The drug should not be used in pediatric patients with closed epiphyses. 2. The drug should not be used in patients with symptoms of tumor progression. 3. The drug should not be used in critical patients with severe systematic inflammation during the acute shock period. 【PRECAUTION】 1. The drug should be used in patients with definitive diagnosis under the guidance of doctors. 2. Diabetic patients may need to adjust the anti-diabetic drug doses. 3. Patients with growth hormone deficiencies caused by brain tumor or patients with a history of intracranial injury must be closely monitored for the possibility of potential disease progression or recurrence. 4. The simultaneous use of the recombinant human growth hormone and the glucocorticoid may inhibit the growth promoting effect of the growth hormone. Thus, the patients lack of the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) should adjust the dosage of the cortical hormone to avoid its inhibitory effect on the growth hormone. 5. During the treatment period, few patients may develop hypothyroidism, which should be timely treated to avoid negative impacts on the efficacy of growth hormone. Therefore, patients should check thyroid function regularly and take thyroxine supplement when necessary. 6. Patients with endocrine disorders, including the growth hormone deficiency, are likely to suffer from the femoral epiphyseal plate slippage. Patients who appear to walk with a limp during the treatment period should be further assessed. 7. Growth hormone can sometimes lead to excessive insulin secretion. Therefore, attentions must be paid to whether the patients have decreased glucose tolerance. 8. Avoid overdose. An excessive injection of growth hormone can cause a low blood sugar, followed by a high blood sugar. A long-term excessive injection can lead to symptoms and signs of acromegaly and other reactions associated with excess growth hormone. 9. Injection sites should be changed frequently to prevent injection site fat atrophy. 10. Athletes should use in caution. 【FOR PREGNANT AND LACTACTING WOMEN PATIENTS】 Pregnant and lactating female patients should not use the drug. 【FOR CHILDREN PATIENTS】 The recommended dose for hypodermic injection is 0.1IU/kg/d, or as directed by the doctor's advice. 【DRUG INTERACTION】 The simultaneous use of the recombinant human growth hormone and the glucocorticoid may inhibit hormone responses, thus, the dosage of the glucocorticoid during the recombinant human growth hormone therapy should not be more than 10 ~ 15 mg hydrocortisone/m2 body surface area. The use of androgenic steroids can further increase the growth rate. 【OVERDOSAGE】 Avoid overdose. An excessive injection of growth hormone can cause a low blood sugar, followed by a high blood sugar. Long-term excessive injection can lead to symptoms and signs of acromegaly. 【PHARMACOLOGY & TOXICOLOGY】 This recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) has the same effect of the human growth hormone (hGH), which can cause the tibia growth, cartilage growth, and weight gain in pituitary-removed rats. According to the mouse acute toxicity study results, no death is observed when the dose is up to 400 times the clinical recommended dosage. When giving the rats rhGH subcutaneously for 30 days, the results show that except weight gain all other parameters are within the normal ranges, when the dose is up to 50 times the clinical dosage. No pathological and histological changes are observed. The results of the mutagenic test (Ames test), reproductive toxicity test, delayed-type hypersensitivity test are negative. 【PHARMACOKINETICS】 According to the literature, subcutaneous and intramuscular injection have the same effect of drug delivery. Subcutaneous injection can lead to a higher serum GH concentration than that of the intramuscular injection, but the concentrations of IGF-1 are similar. Generally, the absorption of GH is slower, with a Tmax of 3-5 hours and an elimination half life of 2-3 hours. GH is metabolized and eliminated by the liver or kidney. The clearance of GH is faster in adults than in children. The amount of GH directly excreted by urine is extremely small. In the blood circulation, GH binds to the high-affinity GH binding protein (GHBP), resulting in an extended plasma half-life of GH. Different injection times will not affect the concentration of serum GH. However, the drug is usually injected at bedtime to simulate the natural physiological changes of GH secretion (GH level peaks at night). 【STORAGE】 Preserve in well closed containers, protected from light and stored at a temperature of 2℃ to 8℃. 【PACKAGING】 Tube vial, 10 vials/ box 【SHELF LIFE】 24 months |